Easy Definition of Business Economics
Business Economics Definition
Business Economics quantifies the application of Microeconomics theory and concepts in determining the policies of business and development of its strategies and determine how much is the impact of a certain change in an economic factor on the profitability or revenues of a given business and use this analysis in steering the firm's decision-making.
It helps in developing a viewpoint from all the stakeholders' perspectives, be it the employees or the suppliers of raw materials, and also the variables on the demand side i.e. the consumer. Keeping everything in mind, a business develops its vision of how to use its limited resources to create the maximum wealth for all of its stakeholders.
Another important aspect of business economics is that it is an assimilation of positive and normative economics because, it aims at analyzing the market in an objective manner, which is close to positive economics, and at the same time, it deals with formulating the business' decision-making policies which are subjective and resound the goal orientation or perspective of the business, which is close to normative economics Normative economics refers to economists' opinions about what they believe. It may be true for some, but false for others. Furthermore, the statements mentioned under normative economics cannot be verified or tested. read more .
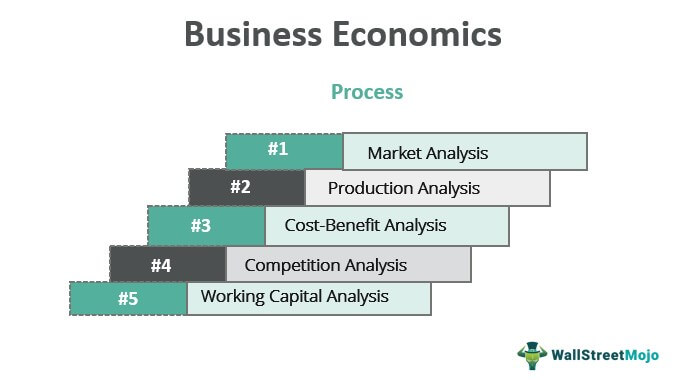
Process of Business Economics

You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Business Economics (wallstreetmojo.com)
Following breakdown is only for understanding, but the process is generally not sequential, and a lot of these steps take place simultaneously in the real world:
#1 – Market Analysis
A business needs to constantly monitor the market for any change in the demand or the quantity demanded of its products. Using this surveillance, the business constantly modifies its level of production and also the factors of production required for producing the forecasted level.
#2 – Production Analysis
Once the market analysis is complete for a predetermined period of time, the business develops a production plan and takes the decisions of the optimum way for the fulfillment of the forecasted demand. If the business expects a very high future demand, it would think of sourcing the raw material directly from the suppliers rather from an intermediary to avail bulk discounts and vice-versa.
#3 – Cost-Benefit Analysis
Once the business is able to estimate the costs of production after receiving the demand forecast, it turns to the pricing policy for its products. Herein, it brings together the costs and benefits to arrive at the desired profit percentage The profit percentage formula calculates the financial benefits left with the entity after it has paid all the expenses. Profit percentage is of two types - markup expressed as a percentage of cost price or profit margin calculated using the selling price. read more . This also encompasses the Break-even analysis Break-even analysis refers to the identifying of the point where the revenue of the company starts exceeding its total cost i.e., the point when the project or company under consideration will start generating the profits by the way of studying the relationship between the revenue of the company, its fixed cost, and the variable cost. read more , which gives the business a target toward which it focuses its resources.
#4 – Competition Analysis
However, the above analysis in isolation can be misleading until and unless the competition dimension is not analyzed. If a firm knows that there are several players in the market then the achievable profit percentage is lower than the desired one, or on the other hand, a monopoly firm may have an achievable profit percentage higher than the desired one
#5 – Working Capital Analysis
Having estimated all of the above factors, the business also needs to consider the amount of running capital required to actually make things happen. The business may bargain on longer credit period policy from its suppliers and shorter collection period of credit sales, or maybe all-cash sales. Most businesses have the mantra of lowering current assets Current assets refer to those short-term assets which can be efficiently utilized for business operations, sold for immediate cash or liquidated within a year. It comprises inventory, cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, etc. read more and increasing current liabilities Current Liabilities are the payables which are likely to settled within twelve months of reporting. They're usually salaries payable, expense payable, short term loans etc. read more so that a higher level of working capital is available in hand and the running of a business is smoother.
Several key decisions choices in a business such as 'make or buy', 'own or lease', 'capital expansion or technological innovation', fall under the foray of business economics as it combines the economic view with the vision of the business and enables the entrepreneur or the management to make an informed decision.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Business Economics (wallstreetmojo.com)
Example of Business Economics
Initially, when Uber started, it didn't plan to be high on fixed investment because at that time it was not sure of how much market penetration Market penetration is calculated as how much the product or service is being used compared to its total market and how it creates a position in the market, especially in the primary stages of setting up the business. read more will it attract. Therefore, it began with a business model of an aggregator, where it connected riders to drivers, who drove their personal cars as and when they could. These drivers were paid on a weekly basis per ride terms.
As its market grew, Uber transitioned to a policy, where it connected drivers to car fleet owners and hired drivers on a permanent basis so that it could fulfill as many rider requests it received rather, being dependent on the availability of the drivers.
This transition has concepts of business economics engrained into it. On analyzing the market, Uber realized that it should increase supply and after conducting a cost-benefit analysis and that for the opportunity cost The difference between the chosen plan of action and the next best plan is known as the opportunity cost. It's essentially the cost of the next best alternative that has been forgiven. read more of the lost revenue, it came to a conclusion of expanding its employee base so that it could fulfill increasing ride demands.
Advantages & Limitations of Business Economics
As with most processes, there is a trade-off between a planned approach and the available resources, and each has its pros and cons, as explained below. A business needs to know how to strike the right balance thereby achieving what's best from its goal orientation point of view.
- Planning and Structure: This process brings a structure to the business and all the policies are aligned to the same, therefore it leads to minimizing the idiosyncratic errors and fortifies the business for the upcoming stages of the economy
- Current and Future View: As the business works in a planned manner, it manages its resources in a way, that fulfills the current requirements and also foresee future requirements. It sets aside certain resources for short term and long term objectives so that when the time comes, it is not short on funds.
- Only an Estimate: Although this process attempts to foresee the various economic factors Economic factors are external, environmental factors that influence business performance, such as interest rates, inflation, unemployment, and economic growth, among others. read more that affect the profits or revenues, it cannot predict the unforeseen events and it is only an estimate which may be misleading. A sudden disruption might lead to all the estimates going off. Therefore the process of business economics doesn't bring absolute surety.
- Not Always Easily Achievable: In theory, it is simple to chalk out a process but in actuality, predicting the demand is not an easy process. At times businesses may not know what is causing the demand and therefore predicting the same becomes next to impossible.
- Time and Cost-Sensitive: As the process is time-consuming, the decision-making may often lag behind. Speeding up the process may require huge investments in the skilled workforce or research infrastructure, which might be cost-intensive. Therefore not all businesses can afford this process, it depends on the stage in the lifecycle of the business, whether or not can it actually apply the planning process to its day to day activities.
Conclusion
Business economics merges the theory of economics with business decision making, to optimize the use of limited resources and achieve the goals and objectives in a structured manner. It is both positive and normative in nature.
Although beneficial, its real-world applicability may not be achievable for every business due to cost and time constraints, however, it attempts to minimize the avoidable losses thereby reducing the possibility of error.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Business Economics and its definition. Here we discuss an example and process of Business economics along with advantages & Limitations. You may learn more about our articles below on Economics –
- Types – Business Transaction
- Formula for Microeconomics
- Explain Behavioural Economics
- Explain Economic Recession
Easy Definition of Business Economics
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/business-economics/
0 Response to "Easy Definition of Business Economics"
Post a Comment